As seen with other highly intelligent animals such as apes and elephants, cetaceans often exhibit stereotypical or abnormal behaviour. Repetitive in nature, this behaviour has no obvious goal or function and is thought to be a result of boredom, distress, and frustration related to an unnatural environment. As a cetacean’s natural repertoire of behaviours cannot be satisfied in a barren concrete tank, they may try to reduce the resulting tension by developing destructive behaviours such as self-stranding for prolonged periods of time, biting on metal gates/chewing at the environment, vomiting and self-mutilation, or non-beneficial behaviours such as comatose-like states/lethargy, head bobbing and pacing/circling.
Self-stranding is a particularly notable stereotypical behaviour due to its potential to become life-threatening. In captivity, cetaceans are taught to beach themselves on concrete slide outs to present themselves to an audience, or to participate in husbandry behaviours such as having their weight taken. This taught behaviour quickly becomes an abnormal habit as cetaceans have been seen to repetitively slide out and lie motionlessly on concrete surfaces for up to 30 minutes. Killer whales, the largest species of cetacean in captivity, can weigh up to 22,000 pounds. Once beached, the orca’s weight begins to slowly crush its internal organs and damage its muscles, causing stores of myoglobin to be released. Travelling in the bloodstream, the protein reaches the kidneys where it is highly toxic. After a prolonged period of time, the damage to their kidneys is irreversible. Re-entry into the water allows their blood to circulate more freely, and this carries even more myoglobin to the kidneys leading to severe kidney damage.
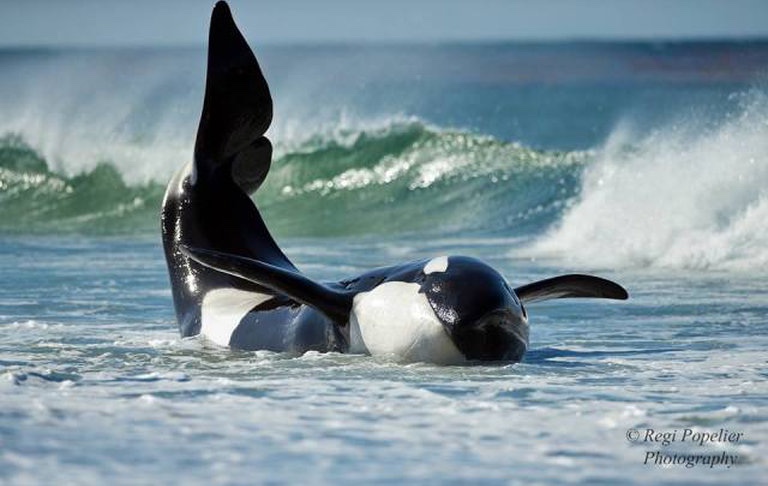

Additionally, on top of this risk, beached cetaceans can also perish from dehydration and heat exhaustion. Their thick layer of blubber and the lack of water causes cetaceans to overheat, become dehydrated and dry out. In February 2016, Morgan, a female orca at Loro Parque, intentionally beached herself on a slide out for around 10 minutes.
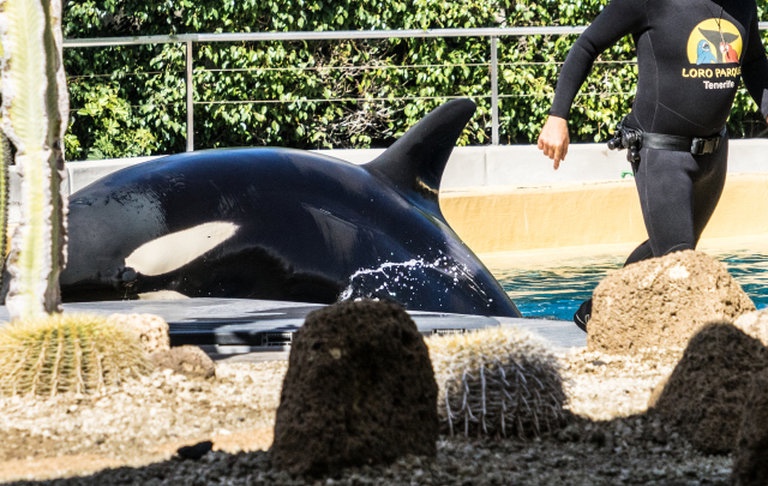

Photo credit to Georg Volk.
Within this time, the skin around Morgan’s melon dried out in 19°C heat. Following this incident, Kelly Flaherty Clark, SeaWorld Orlando’s director of animal training, admitted she’s seen orcas “slide out for 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 15 minutes, even 30 minutes, on their own.” If Morgan’s skin can dry out in 10 minutes in 19°C heat, it’s unimaginable how damaging this abnormal behaviour can be if performed for 30 minutes at SeaWorld Orlando, Florida, which regularly sees temperatures of up to 28°C.
In the wild, only one small population of Patagonian transients in Argentina intentionally strand themselves for hunting purposes. Consisting of around 22 individuals, the whole population was taught how to perform the unique hunting technique by two male orcas named Mel and Bernardo. This cultural behaviour is passed down from generation to generation of Patagonian mammal-eating orcas and, as no captive orcas originate from this population, it’s completely unnatural for the behaviour to be replicated in captivity. Kshamenk, a bull orca at Mundo Marino, is indeed an Argentinian transient but it is unclear whether he is directly related to the stranding orca pod.
Despite not originating from Patagonian transients, orcas at Kamogawa SeaWorld seem to be avid participants in this behaviour, as do various other species of cetacean trapped in Japan’s often horribly inadequate tanks.
Other damaging abnormal behaviours include wearing the teeth by chewing at the environment and regurgitating food. It’s common for under-stimulated and bored orcas to “chew” metal bars and mouth concrete pool corners, like the main stages and concrete slide outs, consequently causing their teeth to become worn, chipped and broken.

Photo courtesy of the Free Morgan Foundation.
Following feeding sessions, captive orcas have been seen to regurgitate their food and play with it. Although this may provide the orca with some stimulation, obsessive regurgitation can lead to health problems as the corrosiveness of stomach acid can damage the lining of the oesophagus as well as already worn teeth. According to John Hargrove, a former senior trainer, all of the whales at SeaWorld Orlando, SeaWorld San Antonio and Marineland Antibes frequently regurgitated their food, to the point that it became a notable problem. Trainers at Marineland Antibes attempted to discourage the behaviour by mixing spiny mackerel (a fish with painful spikes) into their food to make regurgitation painful, and therefore less appealing. However, unwilling to give up their harmful habit, the orcas figured out how much spiny mackerel was in their food, when they ingested it, and when it was less painful to regurgitate it.
Perhaps the most worrying of all abnormal behaviours witnessed in captivity is self-mutilation. There are various ways a cetacean can harm itself in a captive environment but the most commonly observed behaviour is for a cetacean to ram its head or body into the walls or gates of its tank. A particularly disturbing example of self-mutilative behaviour in captive orcas would be the behaviour of Hugo, a male Southern Resident killer whale who was captured from the wild in February 1968 and housed at Miami Seaquarium. Prior to being moved to “The Whale Bowl” (the tank that currently houses Lolita), Hugo was housed in “The Celebrity Pool” which is so small that it now houses manatees.
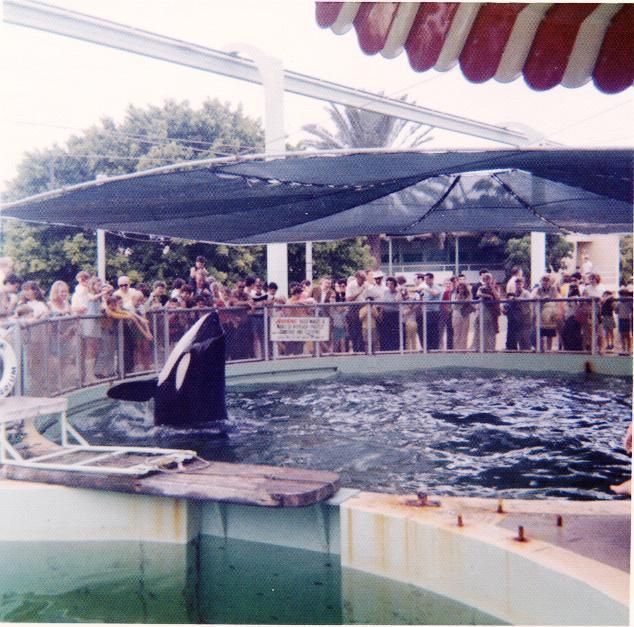
Photo provided by twoodward123.
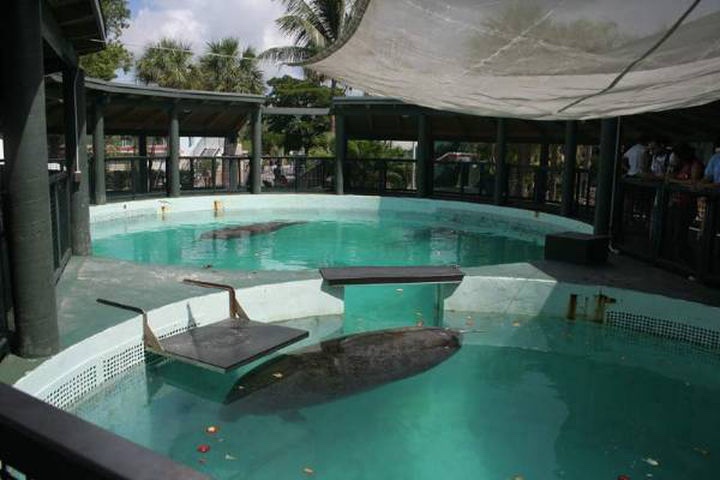

Photo credit to Miami Dade.
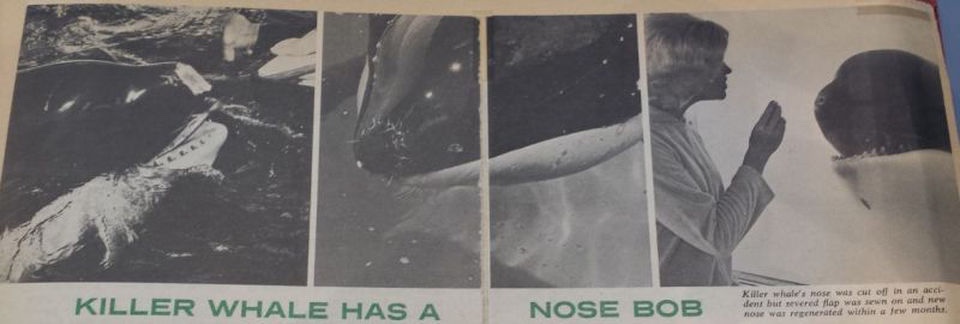
During his stay in this pathetic pool, Hugo developed self-harming behaviour that consisted of him slamming his body into the tank walls. This resulted in a nasty injury on October 1st, 1970 when he slammed his head into the circular ‘acrylic bubble’ feature of his tank and punctured a five-inch hole into it.

Photo provided by Cassie.
The acrylic sliced off approximately two-inches of his rostrum. Hugo had to undergo a 45-minute operation without a local anaesthetic for his severed flesh to be stitched back onto his rostrum. Despite his veterinarian’s best efforts, the sewn-on tissue turned completely white, died and fell off completely after seven days, although Hugo did make a full recovery within just four months.
Courtesy of Derangedhyena-Delphinidae (Tumblr)
Hugo’s self-harming behaviour continued when he was placed in The Whale Bowl with Lolita. On March 4th, 1980, his behaviour proved to be fatal as he slammed his head into a tank wall and suffered a brain aneurysm resulting in his death. He was just 15 years old.
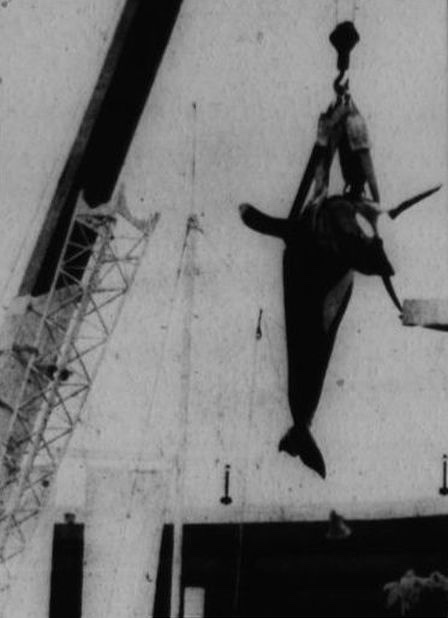

Photo provided by Niki Gianni.
However, self-harming behaviour at Miami Seaquarium did not end with the death of Hugo. As recently as September 2015, multiple bottlenose dolphins who take part in the oceanarium’s “Top Deck Dolphin Show” were seen to repeatedly hit their heads on the bottom of their tank floor. Watch the video below.
Just like Hugo, Kanduke, a Bigg’s transient housed at SeaWorld Orlando, was also known to participate in self-mutilative behaviour. According to Carol Ray, a former SeaWorld trainer, Kanduke would ram himself as hard as he possibly could into the cement walls, metal gates, and glass panels in the show pool on a daily basis. He bloodied his chin, teeth, and rostrum so badly on some occasions that he was not allowed to participate in shows because management said he looked too bad for the public to see. More recently, Skyla, a female orca at Loro Parque, displayed similar behaviour when she breached onto concrete, effectively slamming her body onto the stage, prior to a show.
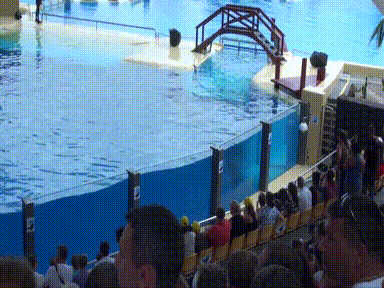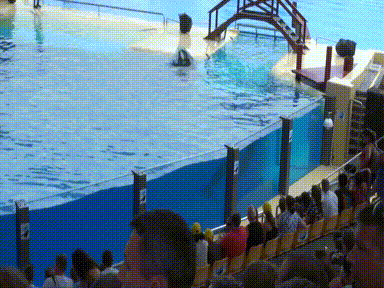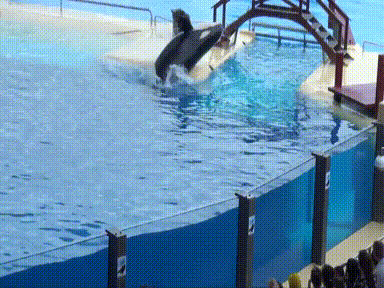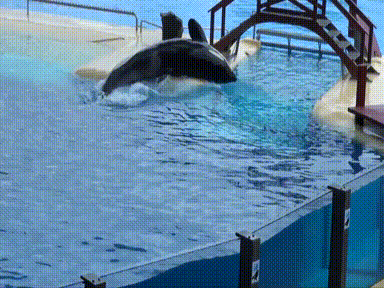
Gif sourced from TBS (YouTube).
Morgan, another female orca at the same facility, repeatedly rammed the gate of the medical pool she was held in after she was separated from her tank mate, Tekoa.
Some captive cetaceans take it a step further and leap out of their tanks, hitting the hard concrete floor below. Kotar, a deceased male orca who resided at SeaWorld San Antonio, reportedly jumped out of his tank twice whilst at the facility, requiring staff to clear and flood the entire stadium so that they could float Kotar back into the pool. In 2002, Hudson, another deceased orca, jumped out of his tank at Marineland Canada during a feeding session. Reportedly unharmed, Hudson was placed on a stretcher and lifted by crane back into the pool. Eight years later in 2010, Kuru, a female false killer whale, jumped out of her tank during a show at Okinawa Churaumi Aquarium. She sustained minor scratches and bruises from the incident.
As recently as 2015, a dolphin jumped out of its tank at Gulf World, landing directly on its dorsal fin. According to former Gulf World trainer, Ashley Guidry, the marine park’s dolphins would jump out of their tanks so frequently that a metal rail was added to the top of the show tanks to try to discourage the dolphin’s dangerous behaviour. It wasn’t uncommon for trainers to come into the park in the morning to find a beached dolphin lying on the concrete walkway beside their tank.
Other abnormal behaviours, such as comatose-like states and logging, are not necessarily harmful when performed, but do carry risks of their own – risks which have been held responsible for contributing to the deaths of two of SeaWorld’s orcas. In captivity, it’s extremely common to see lethargic cetaceans floating motionlessly at the surface, known as logging, or lying perfectly still at the bottom of the pool.
These lethargic behaviours are explained to guests who query it as how dolphins rest. However, although this may be the captivity-adapted version, wild dolphins do not stop moving to sleep. As dolphins must be conscious to breathe, they use unihemispheric sleep, in which they shut down one hemisphere of their brain at a time, to rest whilst remaining alert and able to breathe. Whilst in this state, dolphins remain in close proximity to their pod members, slowly moving forward.
According to Dr. Naomi Rose, a leading marine mammal scientist, it’s “extremely rare” for wild orcas to remain still for a minute or two, unlike captive orcas who log for hours upon hours at a time. Dr. Rose believes this highly abnormal behaviour is the result of “chronic stress, boredom and inhibition of natural behaviours that occurs as a result of inadequate living conditions” at marine parks and aquariums alike. As for captive orca deaths related to this behaviour, Kanduke, a 19-year-old male, died in 1990 with the St. Louis Encephalitis Virus (SLEV) implicated in his death, followed by Taku, a 14-year-old orca, who succumbed to the West Nile Virus (WNV) in 2007. Mosquitoes, who swarm the orca’s exposed dorsal fins and backs when they’re logging, were held responsible for transmitting the viruses.